8 SEO Mistakes You Don’t Want to Be Making by Ronald Dod. Available from <http://smallbiztrends.com/2016/08/fix-seo-mistakes-seo-tips.html>. [August 10, 2016]
The goal of SEO is to get your website ranking in the search results so that it can be found by users, and, when they get to your site, for it to be everything they were searching for. Sounds simple, right? Wrong.
SEO is a constantly evolving art form that takes continuous trial and error to be a master of. It is a complex process that adapts at the speed of light. A great SEO team is constantly working to stay ahead of the game so that they know all of the latest and greatest SEO practices.
What worked six months ago might be completely out of date now. And, while the differences between yesterday and today might be tiny, in this industry, tiny differences can make huge changes. A small mistake could end up tanking your search result rankings, and no one wants that.
Here are eight mistakes that you might be making without even realizing it, and expert tips on how to fix them ASAP.
SEO Tips to Fix Mistakes
Keyword Cannibalization
Don’t let the scary name spook you; keyword cannibalization isn’t that scary at all, but it can have disastrous results. Keyword cannibalization occurs when two or more pages on your website are competing for the same keyword(s). This can occur when people don’t realize that they have duplicate content or duplicate titles, or even when inexperienced SEO “specialists” optimize multiple pages for the same keyword on purpose, thinking it will make the website as a whole more authoritative, but that is not the case.
Keyword cannibalization does nothing but hurt your site. Why? Well, think about it this way. The SERPs are a list; number one, two, three, four, and so on. Logistically, one has to come before the other. Google searches the web and chooses the web pages that are most accurate to the keyword that is being searched in order to rank them.
Now, when Google comes across both (or more) of your pages that are for the same keyword, they are forced to pick one to rank. What if Google picks the wrong page? Something you must always remember when dealing with SEO: Google wants their users to be happy with their search results. If a user doesn’t like your website, then Google isn’t going to, either.
Another thing that you must consider is that Google is just an algorithm — a machine. It’s not a human brain that can make connections or understand what you are thinking. Sure, it’s extremely advanced, and we think of it as all-knowing, but, at the end of the day, you have to manipulate it to understand your website based on the parts that the algorithm will read. If you have multiple pages that all rank for the exact same keyword, Google might not be able to understand that, and it won’t rank any of your pages. That, my friend, would be a complete disaster.
So, what do you do if your website is suffering from keyword cannibalization? There are basically only two options, which depend on your site and your content. The first, you can merge multiple pages if it makes sense to do so. If not, your other option is to un-optimize all other pages except for your main one for each keyword.
Duplicate Content
We touched briefly on duplicate content, but why don’t we go ahead and dive on in. Now, this is somewhat of a controversial topic among SEO experts. Some will tell you that Google does not have a duplicate content penalty. Some will tell you that Google absolutely does have a duplicate content penalty. So, which one is right? In this case, kind of both.
Google has come out and said that there is no penalty for having duplicate content on your site, but that doesn’t mean that it is a good practice or that it can’t hurt you. We see this a lot, because it really comes into play with eCommerce sites, which are some of the worst for doing this. Way too many eCommerce sites will take the manufacturer’s descriptions and titles, and then put them on their own site. In my expert opinion, this is an easy topic: Don’t duplicate content.
While Google has said that there is no “penalty” for duplicate content, they have also said that they value uniqueness. So, will having duplicate content hurt you? Maybe not, but will unique content help you? Absolutely. Our advice to our eCommerce clients is to have unique categories and product descriptions for everything, and if you have separate pages for size and color, merge them together.
Broken Links
Links are golden in this industry. They give your users more information, can help build trust in your authority, and can even build relationships with other people on the web. However, a broken link does nothing. If it wasn’t somewhat obvious, a broken link is a hyperlink that no longer goes to where it was intended. Naturally, over time, links are going to break, and you are going to acquire broken links. Pages go down, sites change; it’s natural.
However, if broken links are a natural part of websites, then why the fuss over them? One or two broken links might not kill your rankings, but you don’t want to accumulate a lot of them. No user is going to appreciate clicking on your link, and it then going nowhere. We all know it’s frustrating, and it generates a bad user experience, which is something Google is passionate about.
Google and users want sites that work. The good news here is that it doesn’t take much to fix this. Check out Broken Link Checker to find any of your broken links, and take them down; and then keep repeating this every now and then. A little housekeeping gradually over time will help you in the long run.
Incorrect Redirects
In the SEO world, a redirect is how you forward one URL to a different URL. This sends users to a separate URL from the one they originally asked for. There are numerous reasons that you use redirects, but the main thing to remember is that you don’t want to have the wrong type of redirect.
You want to use 301 redirects. These are permanent redirects that tell both the searcher and search engine that a page has been moved permanently. Almost more importantly, a 301 redirect will pass at least 90 percent of its ranking power to the new page.
However, you also have 302 redirects, which are temporary redirects. Since Google sees this as a temporary thing, they have no reason to pass on any authority. There are very few times when this should be used. Most of the time, you want to use a 301 redirect, and any 302 redirects that you have could be hurting your rankings and should be changed over.
No Internal Linking
Not only do you want functioning outbound links, you also want to make sure you have internal links to other pages on your website. A lot of websites that I come across don’t do this, which is a shame. Either they think it’s a complete waste of time, or they don’t understand the SEO juice that internal linking can bring. Not only can it help a search engine find more of your pages, but it can also help your users find more of your pages and the information that they might find helpful, which makes them happy. Remember, a happy user, a happy Google.
There are several ways that you can link internally. You can use anchor text to point to another site, or you can use links like “read more” or “click here for more information.” Another great way is to have a “related pages” section at the end so that users can see where else they should go. Generally, you want to have about 3-10 internal links per page. Pages that you want to rank higher should have more internal links than others. Also, make sure you do a little housekeeping here. As you add new pages, you want to make sure you go back to older pages and link them to any new content you have.
Incorrect Title Tags and Descriptions
This has been stressed by almost every expert in the game, even Google, and yet websites do this all the time. All of the pages on your website should have unique, descriptive titles. The title is one of the most important SEO aspects that there is. You cannot overlook this. The title needs to reflect what is on the page, not just the same title as all your other pages.
Meta descriptions are another aspect of SEO at which many websites fail. Again, these need to be unique. Your meta description is the content that appears under your title in the search results. This is your sales pitch. Having a good meta description can greatly increase your CTR. You have 160 characters to tell the searcher what your page is about and how it relates to them. It needs to be persuasive, unique, and highly descriptive.
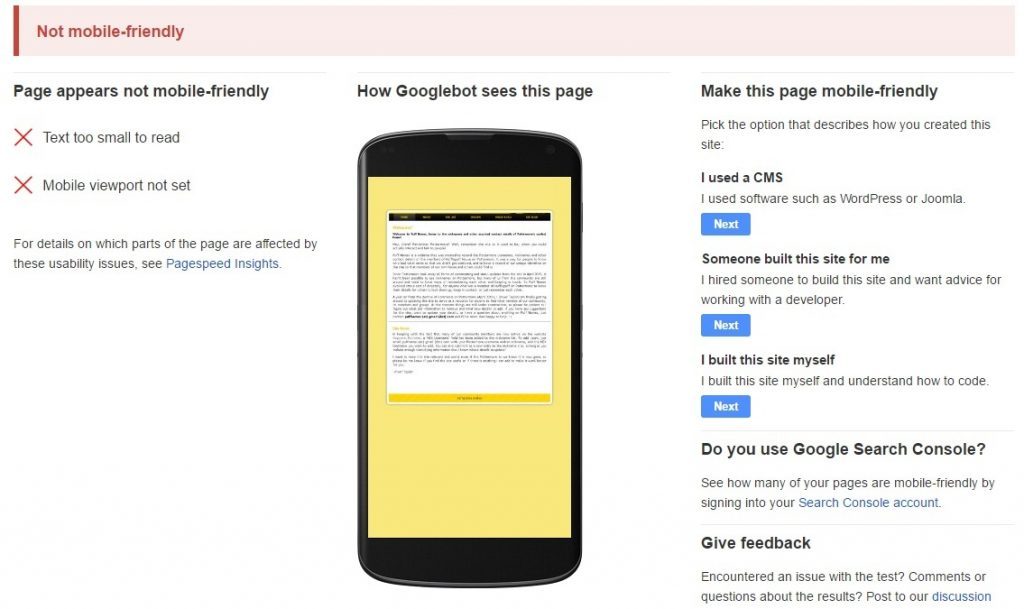
Non-Responsive Websites
Today more than half of all searches happen on mobile devices, and, unless something completely bizarre happens, that percentage is just going to increase. With all of this mobile activity, websites need to make sure that they can perform on those platforms. They need to be responsive — automatically resizing to fit whatever device the user is on. Google has even stated that websites can’t be complacent, and they have to update with the times. In today’s technology-driven world, that means being mobile responsive.
Again, this all goes back to the user experience. You want those who found your site to be able to access it seamlessly, regardless of what device they are on. Now, we will go ahead and let you know that having a responsive website is a pretty big undertaking. It takes a lot of work on the development side, but, in the long run, it is completely worth it.
Slow Site Speed
Let me put this the simplest way I can: A slow website is a terrible website. End of discussion. In today’s technology-saturated and fast-moving world, people want things in a second, and you have about that long to deliver your website to them. It’s generally accepted that a website should load in two seconds or less; any more than that, and the user is going to become frustrated and abandon it.
Google wants the web to be functioning at the speed of light, and, if you can’t deliver that, then you could be punished for it. They have previously indicated that site speed is one of the variables in their algorithm.
At the end of the day, having a slow website can not only affect your SEO, but your conversions and your bottom line. So, you’ve got to speed it up. Test out your site speed now; if it is too low, then you’ve got some work ahead of you. You can work on optimizing your code by decreasing any unnecessary characters, removing redirects (like I’ve already told you to do), working on compressing large files, optimizing images on your site, or using a CDN. Whatever you do, you’ve got to get your site moving faster to give your users a better experience and to rise in the rankings.
Smartphone Photo via Shutterstock
8 SEO Mistakes You Don’t Want to Be Making by Ronald Dod. Available from <http://smallbiztrends.com/2016/08/fix-seo-mistakes-seo-tips.html>. [August 10, 2016]